In today’s digital world, managing data storage management is very important for keeping your business information safe. Companies need data for making decisions and running their operations well. So, it is very necessary to have strong strategies to protect this important asset. This article will explain practical ways to manage and secure your data storage, helping your business stay safe and compliant.
Data Management Solutions
Implementing a Systematic Folder Structure
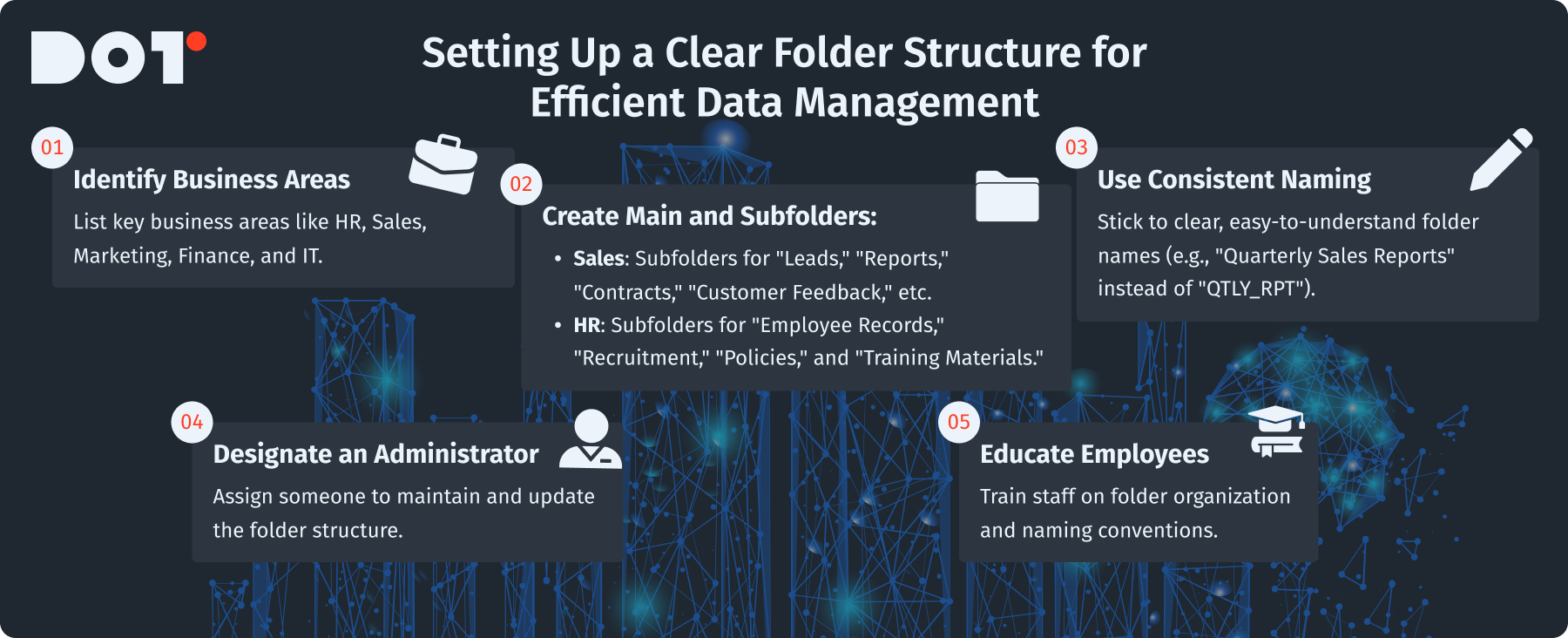
Creating a clear folder structure is very important for managing data efficiently. A well-organized folder system helps employees find files quickly, boosting productivity. By implementing a structured data storage management system, you can ensure that everyone knows where to locate essential documents. Here’s how to set up a good folder structure:
Identify Business Areas:
First, make a list of key areas of your business that need data. Important departments include HR, Sales, Marketing, Finance, and IT.
Create Main and Subfolders:
For each department, make main folders. Under these main folders, add specific subfolders for each department’s tasks.
For example:
- Sales Folder: Make subfolders for “Leads,” “Reports,” “Contracts,” “Customer Feedback,” and “Sales Strategies.”
- HR Folder: Organize folders into “Employee Records,” “Recruitment,” “Policies,” and “Training Materials.”
Use Consistent Naming Conventions:
Be consistent with names. Use clear names for folders that everyone understands. Avoid complicated words or short forms. For example, instead of “QTLY_RPT,” use “Quarterly Sales Reports.”
Designate an Administrator:
Pick a person to manage the folder structure. This person should regularly check the folder system to add, change, or combine folders as needed.
By implementing data organization methods, your team can find files quickly, improving productivity and meeting data management rules. Effective data storage management starts with a solid foundation in document organization.
Utilizing Metadata and Tagging
Metadata and tagging help improve how we find and manage data. Metadata is data about data, like the file’s author, creation date, file type, and keywords. Incorporating metadata into your data storage management practices can greatly enhance searchability and organization. Here’s how to use these tools well:
Define Required Metadata: Figure out what metadata is necessary for your organization. Common types include:
- Descriptive Metadata: Title, author, and subject.
- Structural Metadata: Information about the data structure (e.g., file type, content parts).
- Administrative Metadata: Details about file origin, creation and modification dates, and access permissions.
Implement a Tagging System: Create a tagging system that lets users assign keywords related to the data content. For example, for files on a marketing campaign, use tags like “2023 Campaign,” “Social Media,” “Budget,” and “Target Audience.”
Incorporate Metadata Management Tools: Use tools that help manage metadata. These tools can automatically show metadata, making it easier for employees to use.
By teaching employees to use metadata and tags when saving files, you make it easier to find data, leading to smoother operations. This proactive approach is a key component of successful data storage management.
Have questions about your data organization? Reach out to a Dot Analytics expert for a free 20-minute consultation!
Data Storage Solutions
Conducting a Comprehensive Audit of Existing Data Storage Management Solutions and Security Protocols
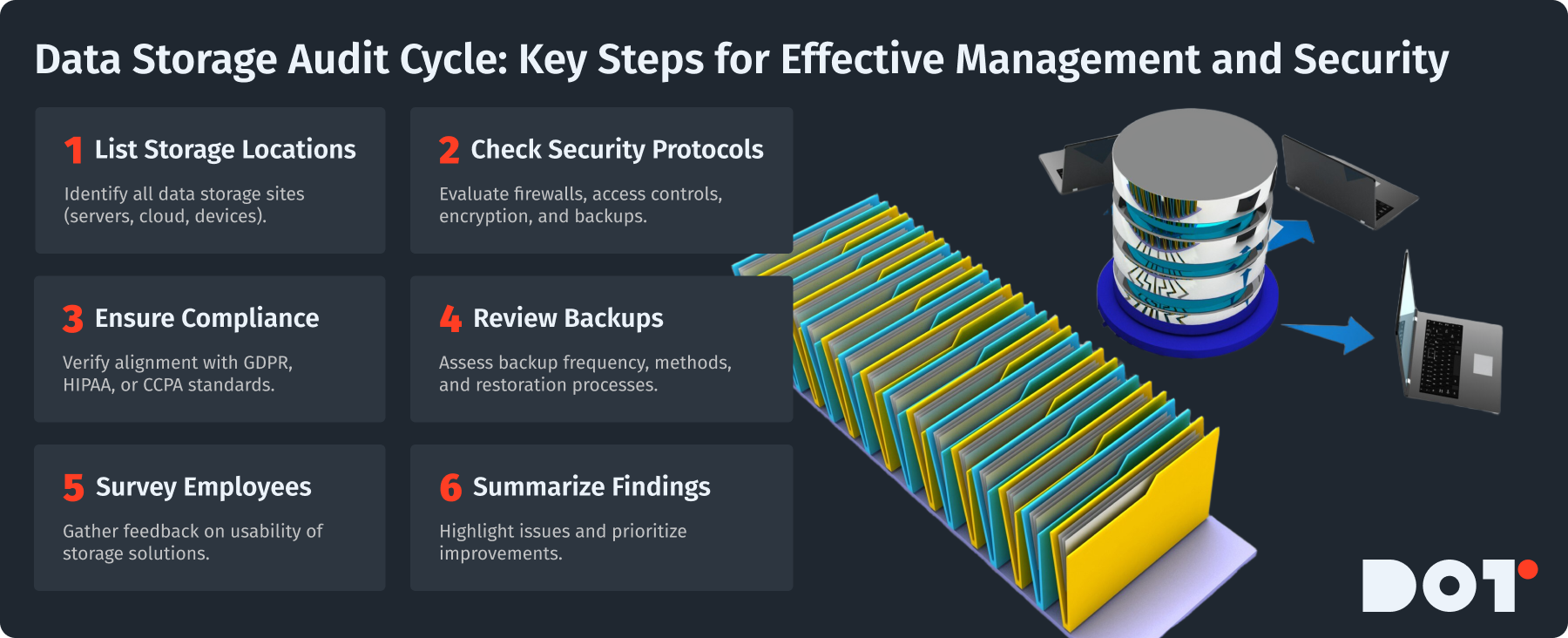
Before making any changes to your data storage, audit your current systems. This helps identify strengths and weaknesses in your data storage management practices. Here’s how:
List All Data Storage Locations:
Write down every place where data is stored, including physical servers, cloud storage, and portable devices.
Evaluate Security Protocols:
Check the security measures in each data storage solution. This includes:
- Firewalls
- Access controls
- Encryption methods
- Backup processes
Assess Compliance Measures:
Make sure your data storage practices meet rules like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Document any needed compliance-related papers.
Review Backup Procedures:
Look at how often data backups happen and the method used (full, incremental, differential). Check if you can restore data from backups easily.
Conduct Employee Surveys:
Get feedback from employees about their experiences with the data storage solutions. This may help find usability problems.
Compile Your Findings:
Summarize the audit results, noting areas needing improvement. Prioritize these for prompt action.
By auditing your systems, you strengthen your data storage management and comply with necessary rules. Regular audits ensure that your data storage management remains effective and secure.
Identifying Gaps in Security That Need Addressing to Enhance Overall Data Protection
Knowing security gaps is essential for protecting your data. You can better identify these vulnerabilities by analyzing your data storage management protocols. Here’s how to find and address these vulnerabilities:
Conduct a Risk Assessment:
Identify potential threats to data security (like cyber-attacks or data breaches). Use a risk matrix to classify threats by probability and potential impact.
Analyze Data Access Controls:
Review who can access sensitive data. Ensure employees have access only to what they need for their jobs. Role-based access controls (RBAC) are essential here.
Test Security Measures:
Conduct penetration testing to check the effectiveness of your security protocols. Identify weaknesses in your firewall, software, and access controls.
Inventory Software and Hardware:
Keep an inventory of your data storage hardware and software. Old software can be a weakness. Plan to update or replace these.
Stay Informed About New Threats:
Cyber-security is always changing. Ensure your team knows the latest threats. Use a cybersecurity consultant if needed.
Develop an Incident Response Plan:
Create a plan for responding to a data breach. Having a usable plan can reduce damage.
By finding security gaps and improving your data storage management practices, you can take steps to improve protection and keep your sensitive information secure.
Data Management Practices
Understanding Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption Solutions
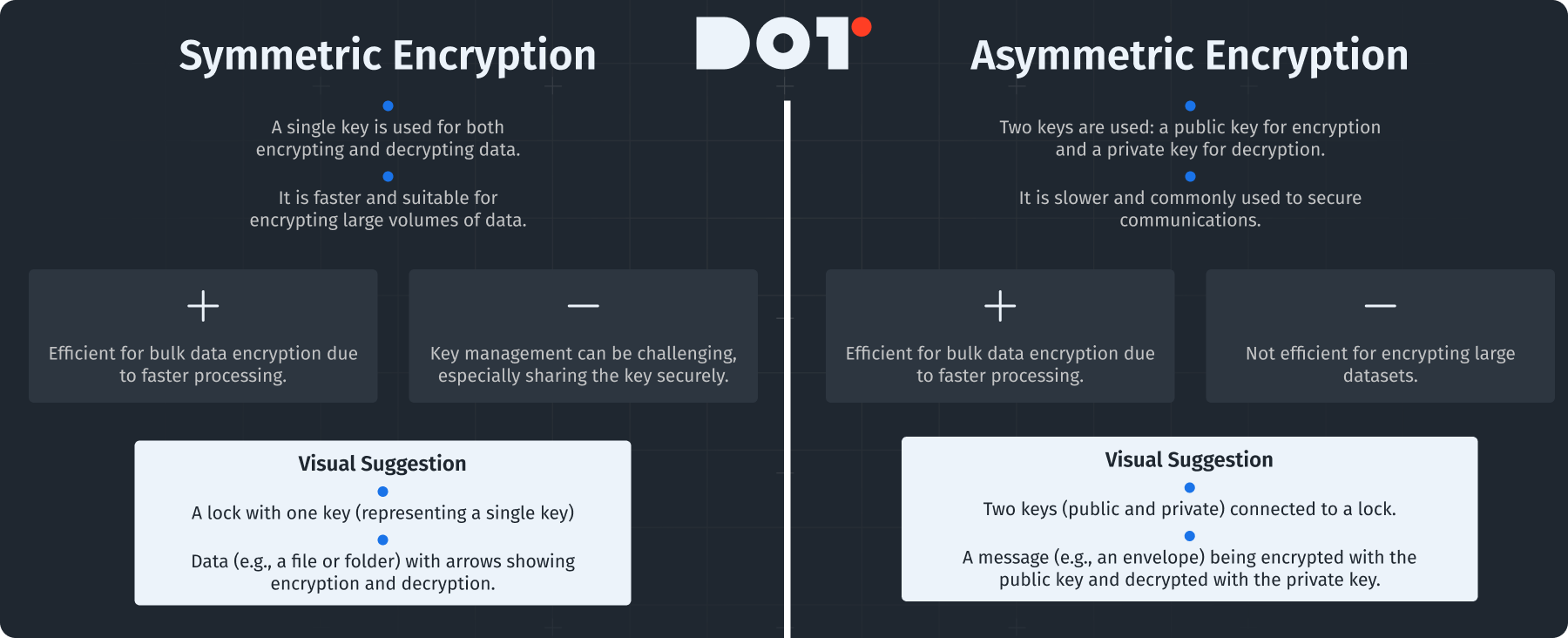
Data encryption is key for protecting sensitive information. Knowing the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption is vital for effective data storage management.
Symmetric Encryption:
This uses one key for both encrypting and decrypting data. It is usually faster and good for large data volumes.
- Benefits: Efficient for bulk data encryption due to faster processing.
- Drawbacks: Key management can be tricky, especially in sharing the key securely.
Asymmetric Encryption:
This uses two keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. It is slower and often used for securing communications.
- Benefits: It solves the key distribution problem since the public key can be shared openly.
- Drawbacks: It is not efficient for encrypting large datasets.
Evaluate your data sensitivity and compliance requirements to see which encryption method is best for your data storage management. Using symmetric encryption for data-at-rest and asymmetric encryption for secure communications often works well.
Choosing the Right Encryption Methods Based on Data Sensitivity and Compliance Requirements
When choosing encryption methods, knowing your data’s sensitivity and legal obligations is key for robust data storage management. Here’s how to go about this:
Assessing Data Sensitivity:
Classify data like public, internal, confidential, and highly confidential. Each needs different protection levels:
- Public Data: No encryption needed (like marketing materials).
- Internal Data: Basic encryption should be in place.
- Confidential Data: Needs strong encryption methods like AES-256.
- Highly Confidential Data: Requires a mix of symmetric and asymmetric encryption plus extra security measures.
Regulatory Compliance:
Look into rules affecting your data practices. Rules can differ among industries:
- HIPAA: Healthcare groups must encrypt health records.
- GDPR: Sets guidelines for processing personal data.
- CCPA: Businesses must protect consumer data.
Choosing Appropriate Encryption Tools:
Research software that offers encryption services related to your needs. Look for:
- Key management capabilities
- Compliance certifications
- User-friendliness
Following these steps helps your organization choose and apply the right encryption methods based on your data storage management needs. A strategic approach to encryption enhances your data’s security.
Need clarity on encryption? Book a free 15-minute consultation with one of our experts!
Business Data Storage Management
Overview of Key Regulations Such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA
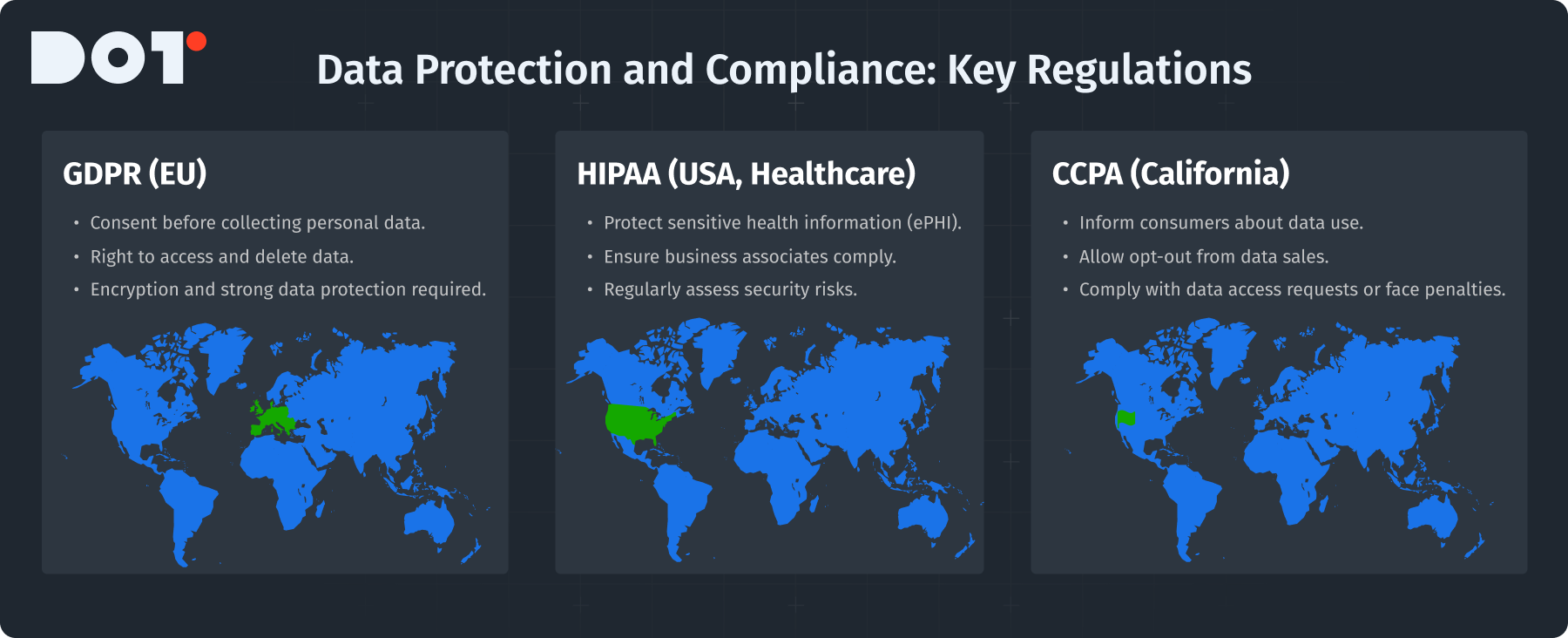
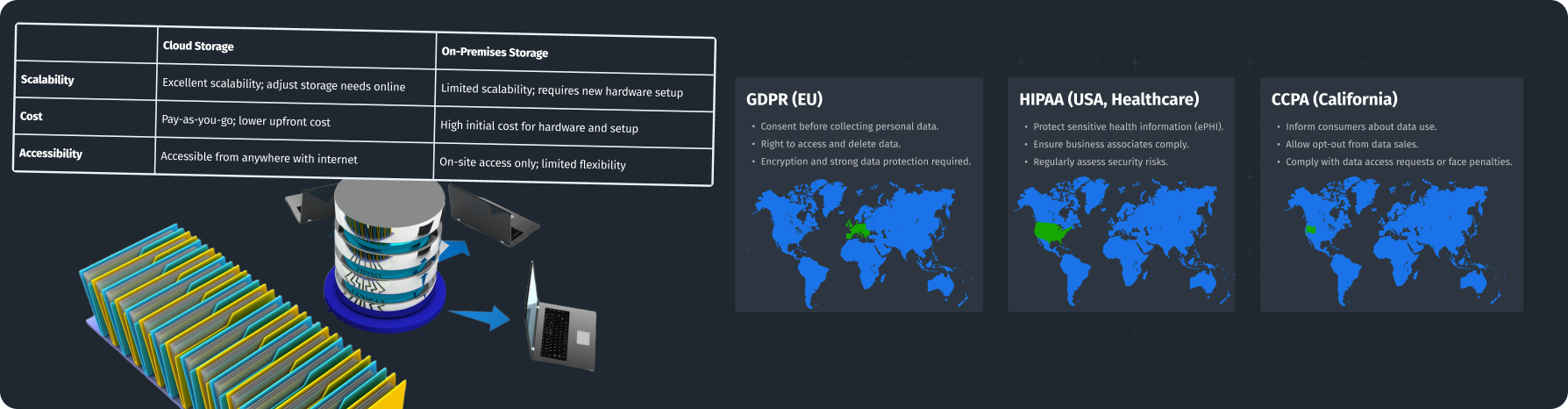
Understanding regulations is crucial for businesses managing data storage. Here are three major regulations that affect data storage management:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Mainly affects businesses in the European Union. It has strict rules for collecting, processing, and storing data, which include:
- Getting clear consent from individuals before collecting their personal data.
- Giving individuals the right to access their data and request deletion.
- Making sure data protection and encryption measures are in place.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Applies to healthcare providers handling sensitive health information. Compliance means:
- Putting security measures in place to protect patient information.
- Ensuring business associates also meet data protection requirements.
- Regularly assessing risks on electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI).
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): Focuses on consumer rights regarding personal data in California. Key requirements include:
- Letting consumers know how their data is collected and used.
- Giving them the choice to opt-out of data sales.
- Penalizing businesses that fail to comply with data access requests.
Each regulation affects how you manage data storage. Knowing their requirements will help you create compliant strategies that enhance your data storage management practices.
Assessing Compliance Implications for Data Storage Practices in Your Business
To ensure your data storage practices meet compliance standards, evaluate your current methods carefully. Here’s a roadmap to improving your data storage management regarding compliance:
Conduct a Compliance Audit:
Check your current data management against compliance rules. Examine:
- Documentation procedures
- Data retention policies
- Access logs to confirm who can view or change specific data.
Develop a Data Protection Policy:
Create a company-wide policy about collecting, storing, accessing, and disposing of data while following compliance rules.
Implement Data Minimization:
Only collect and keep necessary data for your business. Regularly review and remove unnecessary data to streamline your data storage management.
Utilize Technology for Compliance Management:
Use software designed for compliance management. It can help automate data tracking, maintain access logs, and update security measures.
By constantly reviewing compliance aspects, you can create strong rules that safeguard sensitive data and follow regulatory standards, enhancing your overall data storage management.
Effective Data Storage Strategies
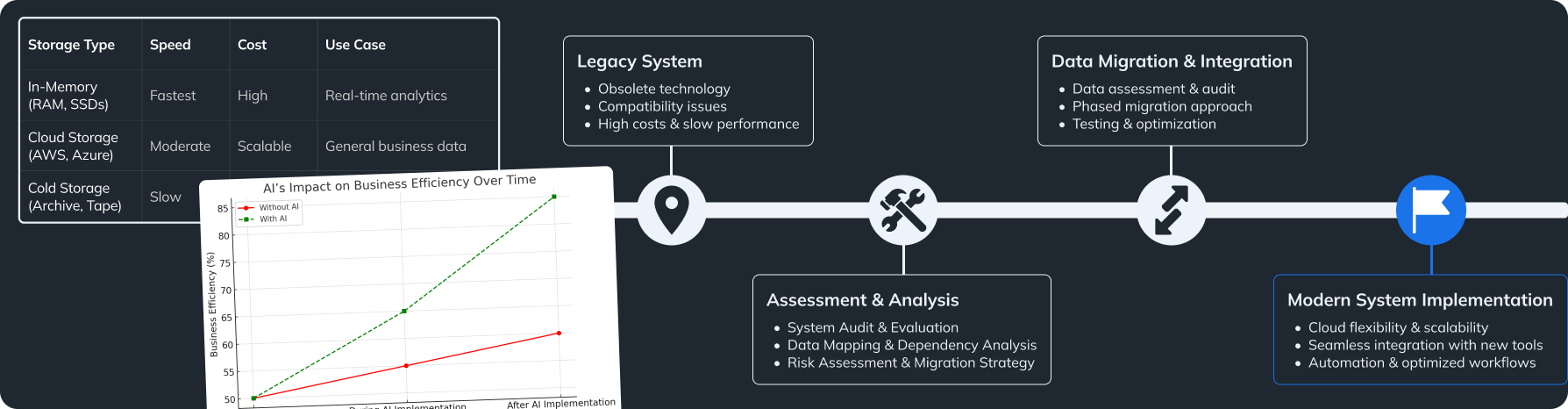
Comparing Scalability, Cost, and Accessibility Between Cloud and On-Premises Data Storage Management Solutions

When choosing the best data storage solutions for your business, it’s important to compare cloud and on-premises options. This comparison is a key aspect of effective data storage management. Here’s a breakdown:
Scalability:
- Cloud Storage: Offers excellent scalability. You can quickly change your storage needs online, perfect for businesses with changing data loads.
- On-Premises Storage: Scaling this is slower and may involve buying new hardware and setting it up, which can be costly.
Cost:
- Cloud Storage: Operates on a ‘pay-as-you-go’ method. You only pay for what you use, cutting down upfront costs.
- On-Premises Storage: Usually has no ongoing costs, but initial setup, including hardware, installation, and maintenance, can be high.
Accessibility:
- Cloud Storage: Allows access from anywhere with internet, great for remote teams.
- On-Premises Storage: Often requires being on-site to access data, less flexible for remote work.
A hybrid solution, combining cloud and on-premises storage, can often give the best balance among scalability, cost, and accessibility in your data storage management plan. Utilizing cloud storage solutions can enhance flexibility and efficiency for businesses today.
Evaluating Potential Risks and Benefits Regarding Security and Data Loss
Understanding the risks and benefits of your data storage methods is key for good data management. By effectively evaluating your data storage management, you can make informed decisions. Here’s how to evaluate these factors:
Identify Risks:
- Cloud Storage Risks: Think about threats like unauthorized access, security breaches, or data loss because of service failures.
- On-Premises Risks: Look at risks from physical theft, hardware failures, natural disasters, or human errors.
Assess Security Measures:
Check if your storage solutions offer good security features like encryption, access controls, and regular backups.
Evaluate Data Loss Scenarios:
Prepare for worst-case scenarios. See how your organization can recover data in case of a breach, whether in the cloud or on-premises.
Understand Benefits:
- Cloud Storage Benefits: Automatic updates, lower hardware costs, and easier team collaboration.
- On-Premises Benefits: Full control over your data environment, potentially better security for sensitive information.
By evaluating these risks and benefits in your data storage management strategy, your business can make informed choices that best serve its security and efficiency. Incorporating data backup techniques is critical for mitigating risks associated with data loss.
Data Governance and Storage Management
Establishing a Backup Schedule That Balances Data Integrity and Operational Needs
Creating a backup schedule is key for keeping data safe while ensuring operations run smoothly. This is a crucial aspect of overall data storage management. Here’s how to create an effective backup schedule:
Determine Backup Frequency:
Decide how often backups should happen based on data sensitivity and business needs. For sensitive financial data, daily backups may be needed, while less critical data might only need weekly backups.
Choose Backup Types:
- Full Backups: A complete copy of all data. It’s thorough but can take time and use a lot of space.
- Incremental Backups: Only back up data that has changed since the last backup. This saves time and space.
- Differential Backups: Back up all changes made since the last full backup, which takes longer but is easier for recovery.
- Create a Backup Calendar: Make a calendar that outlines when backups will happen, who will do them, and what method will be used.
- Monitor Storage Space: Watch backup storage capacities and have a plan for when you need more space.
By designing a smart backup schedule, you assure data integrity while bolstering your data storage management practices. Implementing data retention policies can help guide your organization on how long to keep specific data types.
Exploring Various Backup Methods Such as Full, Incremental, and Differential Backups
Understanding different backup methods is vital for effective data storage management. Here’s a closer look at the methods you can use:
Full Backups:
- Description: A complete backup of all data all at once. This is often used as the main backup before using other types.
- Considerations: It’s easiest to restore everything, but needs the most space and time.
Incremental Backups:
- Description: Only changes made since the last backup are saved.
- Considerations: Faster and needs less storage than full backups, but restoring can be complex since you need the last full backup and all incremental backups that came after.
Differential Backups:
- Description: Captures changes made since the last full backup.
- Considerations: Easier to restore compared to incremental backups, as you only need the last full backup and the most recent differential backup. However, it uses more space than incremental backups.
By exploring these methods in your data storage management, you can choose a backup strategy that fits your organization’s needs. These various data backup techniques can significantly enhance your data protection strategy.
Data Security and Management Practices
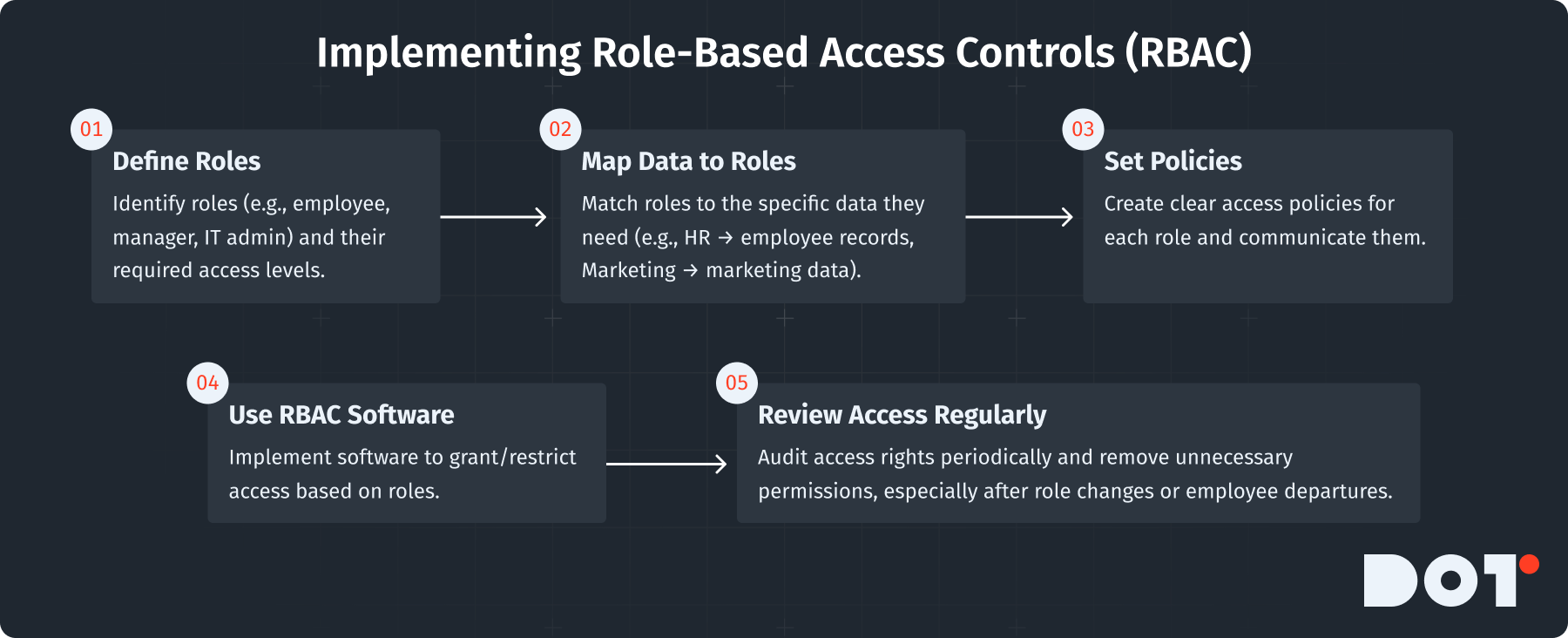
Implementing Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) to Restrict Data Access Appropriately
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is an effective way to manage access to sensitive data in a company. Clear RBAC policies are critical to ensuring proper data storage management. Here’s how to set up RBAC:
- Define Roles: Identify roles in your organization (like employee, manager, IT admin) and what level of access each needs.
- Map Data to Roles: Document which data sets each role should access. For example, HR needs employee records, while Marketing might only need marketing data.
- Create Access Policies: Make clear policies stating what access permissions each role has. Ensure everyone knows these policies.
- Implement Access Controls: Use software that supports RBAC to set access controls. Grant or restrict access based on the roles and policies defined.
By using RBAC, you ensure that sensitive data is accessible only to authorized people, reducing the risk of data breaches within your data storage management framework.
Utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Enhanced Security in User Access
Using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a key part of strengthening data access security. It’s an essential step in any data storage management strategy. Here’s how to effectively implement MFA:
Choose MFA Solution:
Research different MFA solutions available. Make sure it works well with your current systems. Popular choices include:
- Authenticator apps (like Google Authenticator or Authy)
- SMS-based verification codes
- Biometrics (like fingerprint or facial recognition)
Integrate with User Logins:
Work with your IT team to add MFA to your user login process.
Educate Employees:
Train employees on what MFA is, why it’s used, and how to set it up on their devices. Make sure they keep their second-factor devices secure.
Adapt Policies Based on User Feedback:
Collect user experience feedback about MFA and adjust as needed to improve usability without losing security.
Implementing MFA significantly enhances the security of user access to sensitive data and is a fundamental aspect of comprehensive data storage management.
Real-World Applications of Data Management
Case Study: SchoolStatus – Implementing Categorized Data Storage for Improved Educational Outcomes
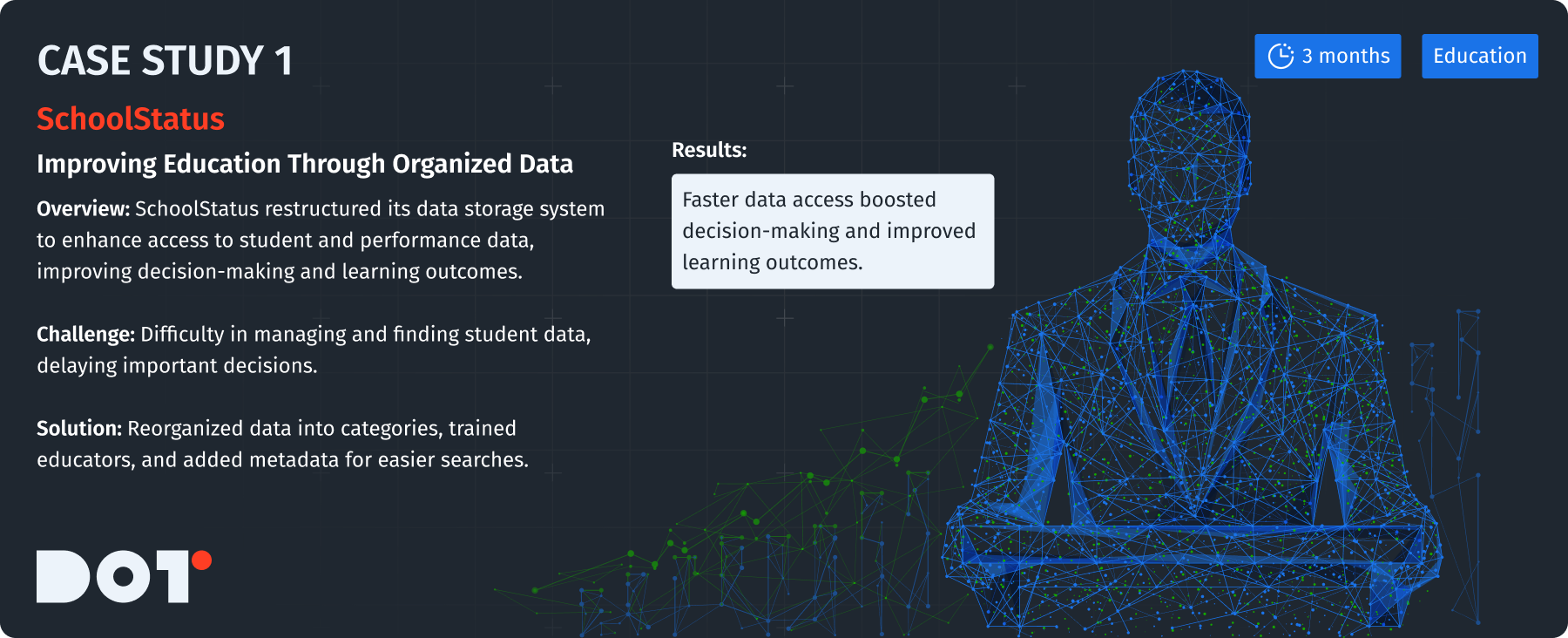
The education platform SchoolStatus had trouble managing a lot of student and performance data. They struggled to find data, which wasted resources and delayed decisions. To fix this, they started a categorized data storage strategy:
- Mapping Out Data Needs: They identified the types of data educators needed, such as attendance, grades, and student feedback.
- Creating a Structured Organization: SchoolStatus reorganized data into categories based on curriculum, student performance, and program effectiveness.
- Training Staff: They trained teachers on using the new organization structure, adding tagging and metadata for better data search. This change supported their overall data storage management goals.
- Continuous Monitoring: They regularly checked data use and refined categories based on changing educational needs.
As a result, educators could improve learning outcomes with faster access to relevant data, boosting decision-making within the school. Their strategic approach to data storage management proved beneficial.
Case Study: Avand Medical – Applying Data Encryption to Protect Sensitive Patient Information
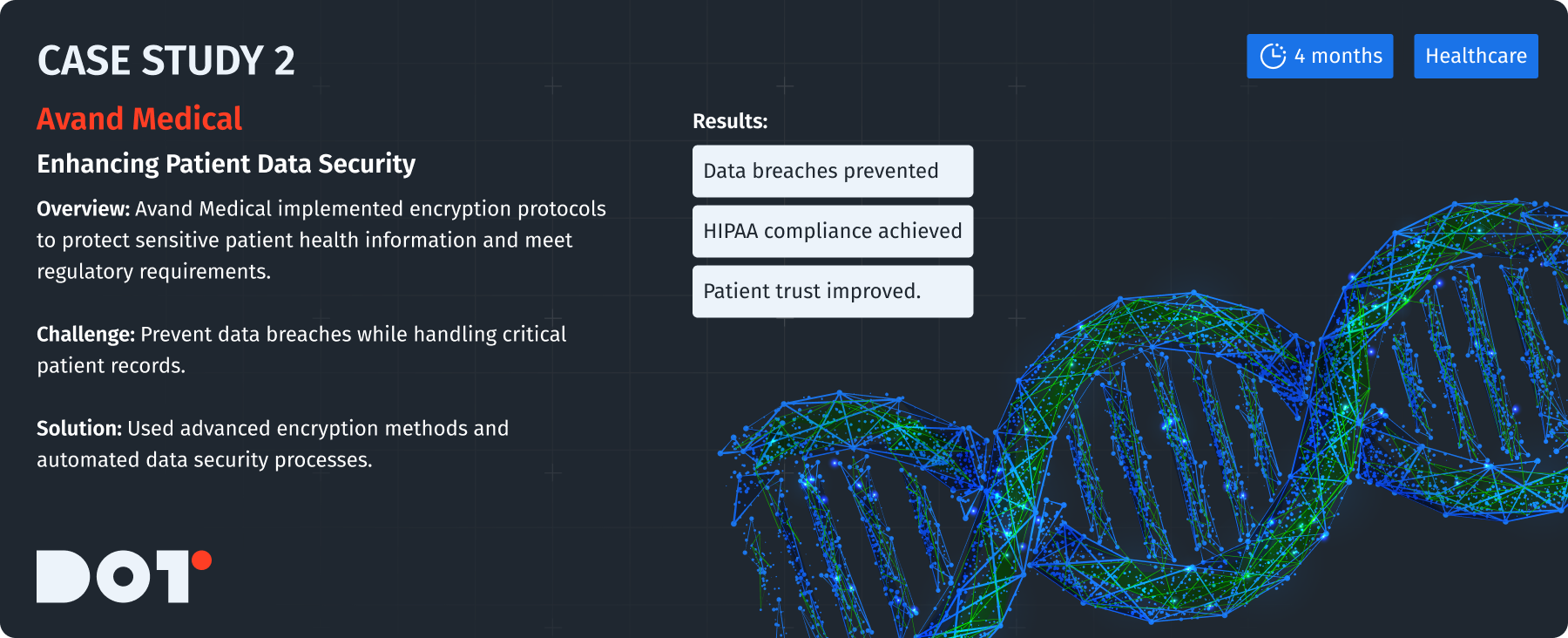
Avand Medical, a healthcare provider, wanted to boost its data security to protect sensitive patient health information. They took steps to integrate encryption protocols as part of their data storage management initiatives:
- Assessing Patient Data Sensitivity: The company categorized health records based on sensitivity, finding the most critical data needing advanced encryption.
- Implementing Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption: They used symmetric encryption for large files and asymmetric keys for secure communications.
- Staff Training on Encryption Policies: Medical staff got training on data encryption to ensure proper handling of sensitive information.
- Ongoing Automation of Encryption Processes: Tools were set up to automatically encrypt data during transfers and storage, reducing human error.
These steps kept patient data safe from breaches and met HIPAA rules, enhancing patient trust and protecting the organization legally, demonstrating the importance of robust data storage management.
Best Practices for Data Organization
Key Practices for Organizing and Securing Data
To organize and secure data well in your business, follow best practices. Here’s a checklist of key practices that are part of effective data storage management:
- Clearly categorize data (like departmental folders or project-based organization).
- Standardize names for easy identification.
- Train employees on data management policies.
- Use metadata and tags for easier retrieval.
- Set access controls and permissions.
- Regularly audit data access and usage.
Steps to Assess Security Measures and Compliance
To check security measures and compliance, do the following:
- Conduct a compliance audit to spot gaps.
- Review access policies for data security.
- Analyze technology and encryption methods currently used.
- Assess employee training for compliance.
- Work with an external expert to compare practices against industry standards.
Interested in how this applies to your business? Schedule a free 20-minute consultation with a Dot Analytics expert!
Recap of Data Management Strategies
Highlighting the Importance of Regular Assessment and Compliance in Data Management
Data management is always changing – technology improves, regulations change, and business needs shift. Regular evaluations keep your data strategies updated, reducing risks and ensuring compliance with data handling laws. The success of your data storage management depends on continuous improvement and adaptation.
Final Thoughts on the Balance Between Security and Access
It’s important to protect sensitive information while ensuring employees can get the data they need to work efficiently. This balance is possible through well-designed policies, regular training, and modern data storage solutions that comply with best practices in data storage management.
Summary
In summary, effective Data Storage Management strategies are vital for keeping business data safe. By organizing data systematically, using metadata and encryption methods, and ensuring compliance, businesses can guard their data from risks.
If you need further insights, feel free to book a free consultation with an expert from Dot Analytics! By proactively managing data storage, your organization can succeed in a data-driven world, protecting your information while enabling efficiency and growth.



















Leave a Reply