Introduction
A first-party data strategy refers to leveraging information that your company collects directly from your customers and users. This data can be obtained through your website, mobile app, CRM system, loyalty programs, and other customer interaction channels. Unlike third-party data gathered from external sources, first-party data belongs to your company and provides deeper insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Why Is First-Party Data Becoming Increasingly Important?
- Tightening Privacy Regulations: Regulatory changes like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) limit the collection and use of third-party data. Companies are compelled to seek alternative, compliant sources of information.
- Phasing Out Third-Party Cookies: Many browsers and operating systems are introducing restrictions on third-party cookies, making it difficult to track users across different websites.
- Marketing Personalization Through Data: Customers increasingly expect personalized experiences. First-party data allows for more accurate audience segmentation and the development of targeted marketing campaigns.
- Increasing Marketing Efficiency: First-party data helps optimize marketing spend and improve ROI.
Purpose of This Article
This article aims to provide marketers with a practical guide on effectively using first-party data strategy. We will cover the following aspects:
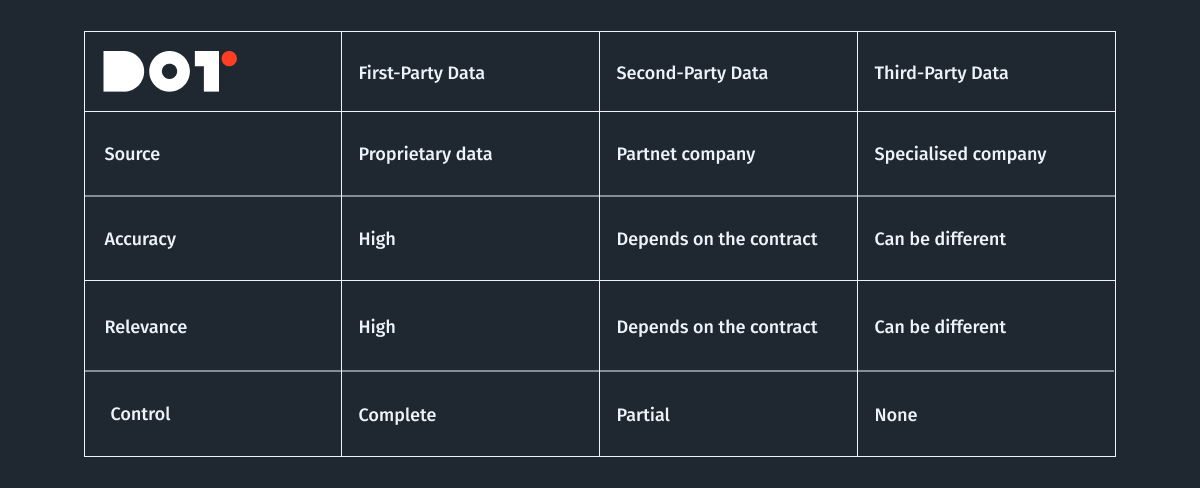
- First, Second, Third-Party Data: Differences, examples, and advantages.
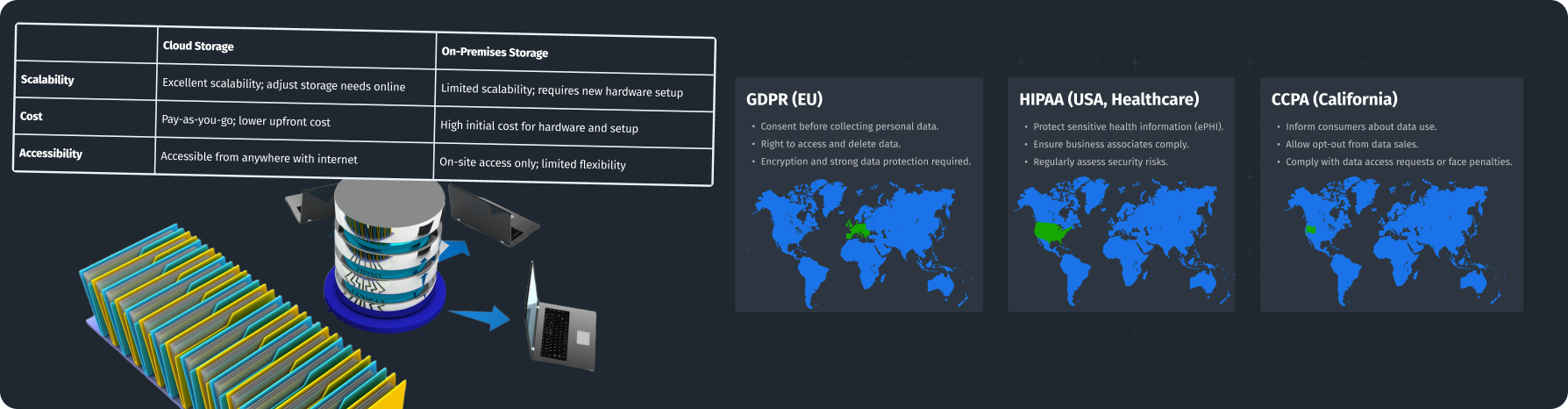
- Collection, Storage, and Legal Compliance of First-Party Data (GDPR, CCPA): What data to collect, how to organize and store it to ensure security and accessibility.
- Implementation Steps for a First-Party Data Strategy: Goal-setting methodology, introduction to Customer Data Platforms (CDP), and integration steps.
- Data Quality and Verification Strategy: Maintaining data accuracy and relevance.
- Addressing Potential Challenges: Common issues and methods to overcome them.
- Examples from Industry Leaders: Demonstrating companies that have successfully implemented first-party data strategies.
- Understanding and effectively utilizing first-party data is key to success in modern marketing. In this article, we’ll explore how to turn first-party data into a competitive advantage and achieve better results in your marketing campaigns.
Do you fully understand the topic? If not, you can book a free 15-minute consultation with an expert from Dot Analytics.
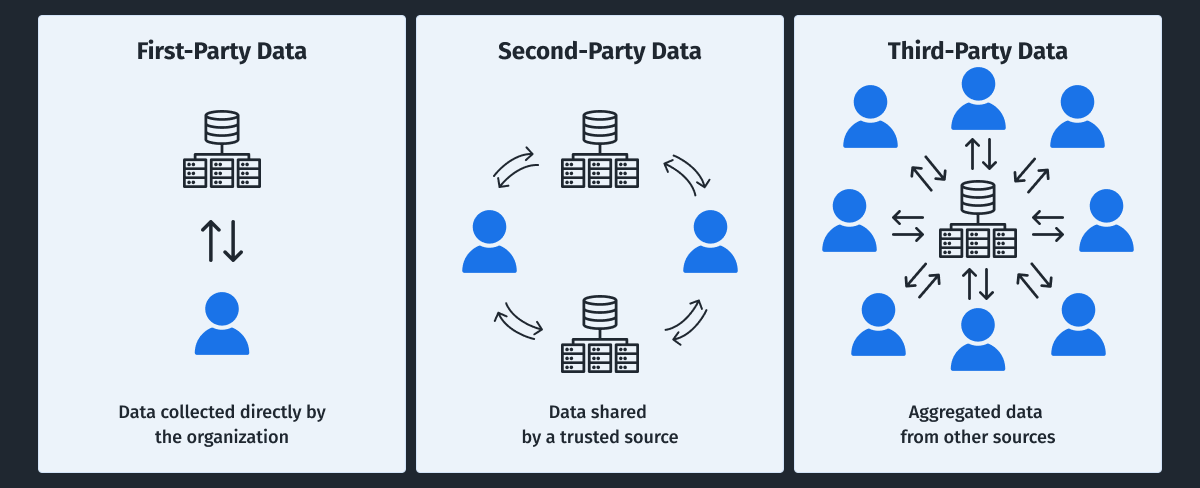
1. What Is First-Party Data?
First-party data is information that a company collects directly about its customers. This can include data obtained through the company’s website, mobile app, CRM system, loyalty programs, and other customer interaction channels.
- Examples: Purchase history, product viewing data, demographic information, interactions with email newsletters.
- Advantages:
- High Accuracy and Relevance: Directly sourced from your audience.
- Control Over Data: You own and manage it.
Second-Party Data
Second-party data is information that one company obtains from another company with which it has a partnership.
- Examples: A company selling children’s products may receive customer data from a diaper manufacturer.
- Advantages:
- Additional Customer Information: Enriches your existing data.
- Expanded Segmentation: Reaches broader audiences.
Third-Party Data
Third-party data is information collected and sold by companies specializing in data aggregation. This data can come from various sources, such as social networks, websites, and mobile apps.
- Examples: Demographic data, online behavior data, and user interests.
- Advantages:
- Large Volume of Data: Access to extensive datasets.
- Market Research: Understanding broader trends.
2. The Strategic Advantage of First-Party Data Strategy
Enhanced Customer Insights and Personalization
First-party data provides companies with a unique opportunity to delve deep into their customers’ world. With this data, marketers can:
- Create More Accurate Audience Segments: By analyzing purchase history, website behavior, demographic data, and other parameters, you can group customers with similar characteristics and needs. This allows for more targeted marketing campaigns.
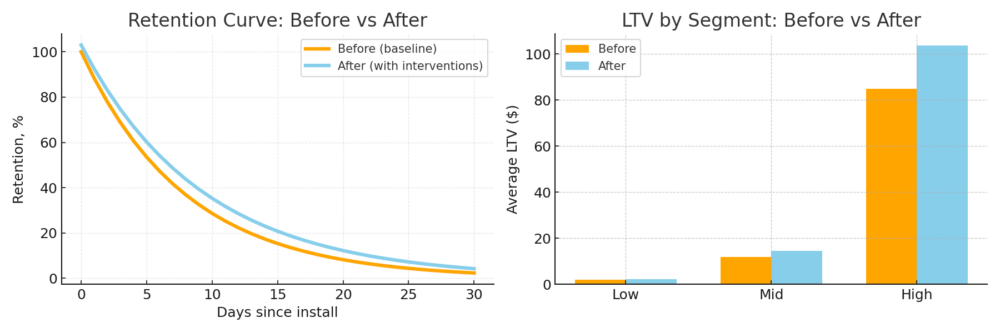
- Develop Personalized Offers: Understanding each customer’s preferences enables you to offer products or services that genuinely interest them, increasing the likelihood of purchase and strengthening loyalty.
- Optimize the Customer Journey: By analyzing the customer journey from the first brand interaction to purchase, you can identify bottlenecks and improve the user experience.
- Predict Customer Behavior: Using machine learning methods, you can forecast future customer actions, such as repeat purchases or churn.
Example: A company selling clothing online can use first-party data to create personalized recommendations for each customer. If a customer frequently buys dresses of a certain color and style, the system can suggest similar models or new collections in that style.
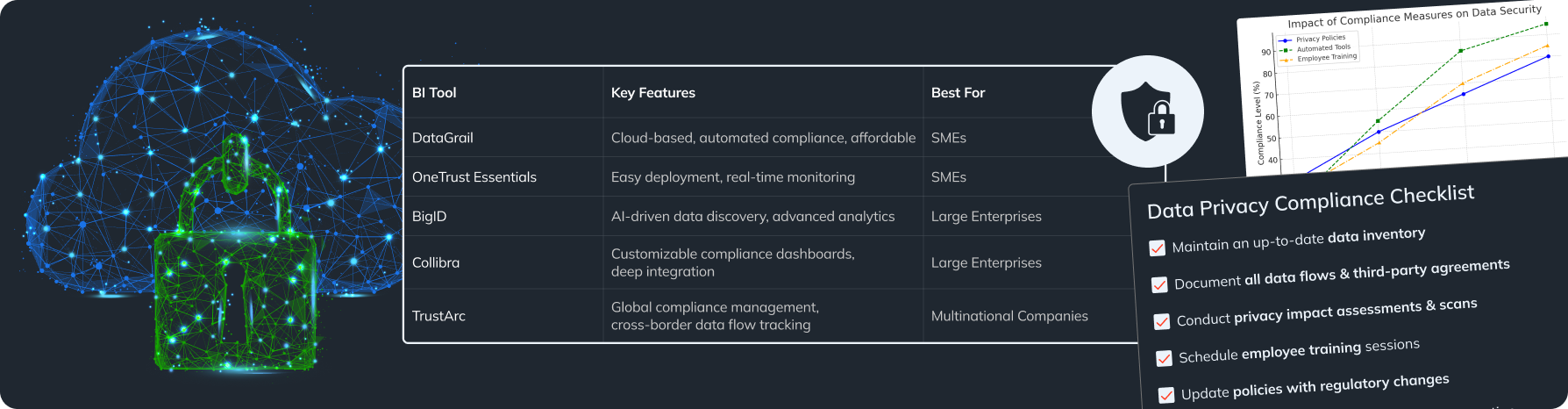
Improved Data Privacy Compliance
Discussing how first-party data aligns with global privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) are key legislative acts aimed at protecting personal data. First-party data collected directly from customers plays a special role in this context.
Why First-Party Data Requires Special Attention
- Direct Interaction: Companies collecting first-party data have more direct contact with customers, implying greater responsibility for protecting their information.
- Data Detail: First-party data often contains deeper and more detailed customer information, making it more valuable but also more vulnerable if leaked.
- Long-Term Storage: First-party data may be stored for years, increasing the risk of compromise.
How to Ensure Compliance with GDPR and CCPA
- Obtaining Explicit Consent:
- Informed Consent: Customers must be clearly informed about what data is collected, how it will be used, and their rights.
- Separate Consent for Each Type of Processing: Different types of data processing (e.g., marketing, analysis) may require separate consent.
- Data Minimization:
- Collect Only Necessary Data: Gather only the data truly needed to achieve your goals.
- Delete Outdated Data: Regularly remove data that is no longer needed.
- Data Security:
- Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
- Access Restriction: Provide data access only to authorized personnel.
First-party data can be a valuable business asset, but its use must comply with personal data protection laws. Compliance with GDPR and CCPA not only reduces the risk of fines but also strengthens customer trust.
Economic Efficiency
Analyzing the economic benefits compared to acquiring third-party data.
- Cost Reduction: First-party data is generally less expensive than purchasing third-party data. Companies can invest in developing their own tools for data collection and analysis.
- Increased ROI: Personalized marketing campaigns based on first-party data typically have a higher return on investment than non-targeted campaigns.
- Improved Decision-Making: First-party data allows for more informed decisions in marketing, product development, and business growth.
3. Developing a First-Party Data Strategy
Setting Clear Goals: The Foundation of a Successful Strategy
Before starting data collection and analysis, it’s essential to clearly define what you want to achieve. It’s recommended to use the SMART methodology:
- Specific: Goals should be clear and specific.
- Measurable: Goals should be quantifiable.
- Achievable: Goals should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant: Goals should be relevant to your company and align with its strategy.
- Time-bound: Goals should have clear deadlines.
Example:
- Incorrect Goal: “Improve marketing.”
- Correct Goal (SMART): “Increase conversion rate by 20% over the next six months by personalizing email newsletters for new customers.”
Structuring Data Collection: What Data to Collect and How
When collecting data, focus on information that will help achieve your goals. However, there are general categories of data that can be useful for most businesses:
- Demographic Data: Age, gender, education, income, location.
- Behavioral Data: Purchase history, website visits, mobile app usage, social activity.
- Psychographic Data: Personal interests, values, lifestyle.
- Financial Data: Income, expenses, credit score.
- Brand Interaction Data: Reviews, comments, participation in surveys.
- Device Data: Device type, operating system, browser.
Data Collection Methodologies
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Conducted online or offline.
- Website and Mobile App Analytics: Collect data on user behavior on websites and apps.
- Social Media: Analyze data from platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram.
- Transactional Data Analysis: Analyze purchase and financial transaction data.
- Interviews: In-depth conversations with customers for qualitative data.
- Focus Groups: Group discussions to gather opinions and perceptions.
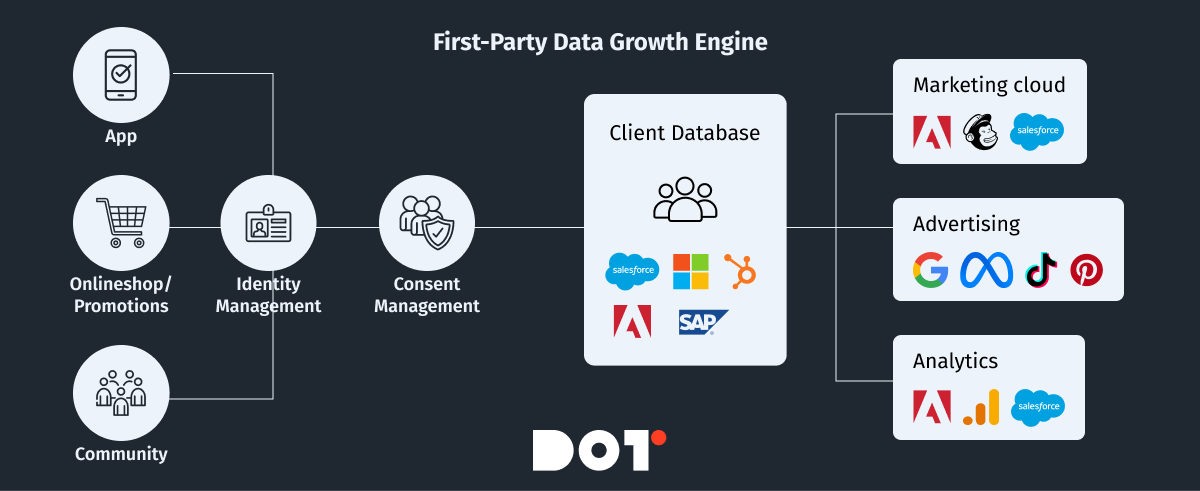
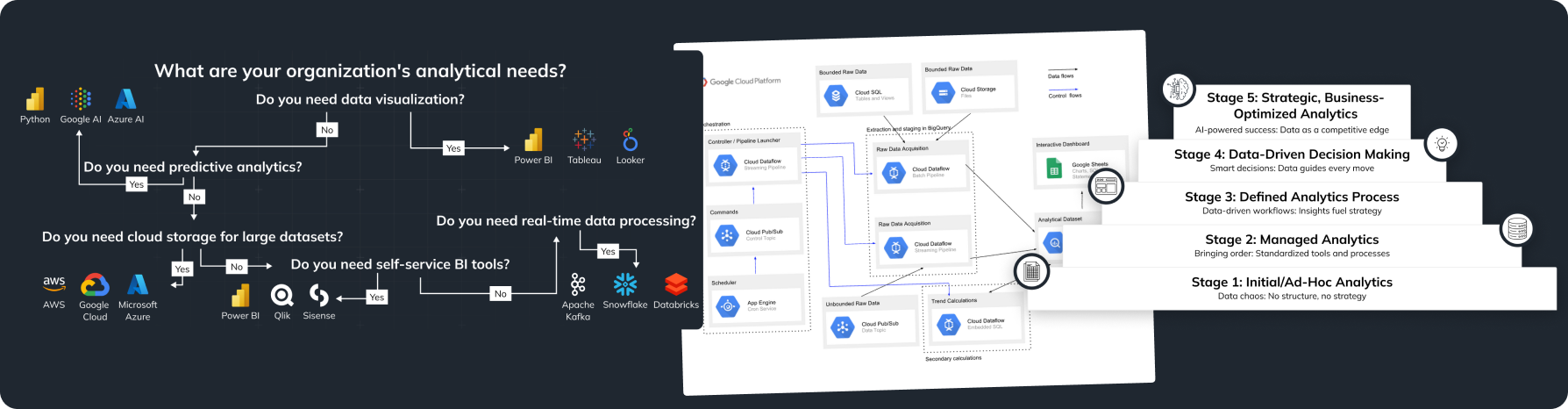
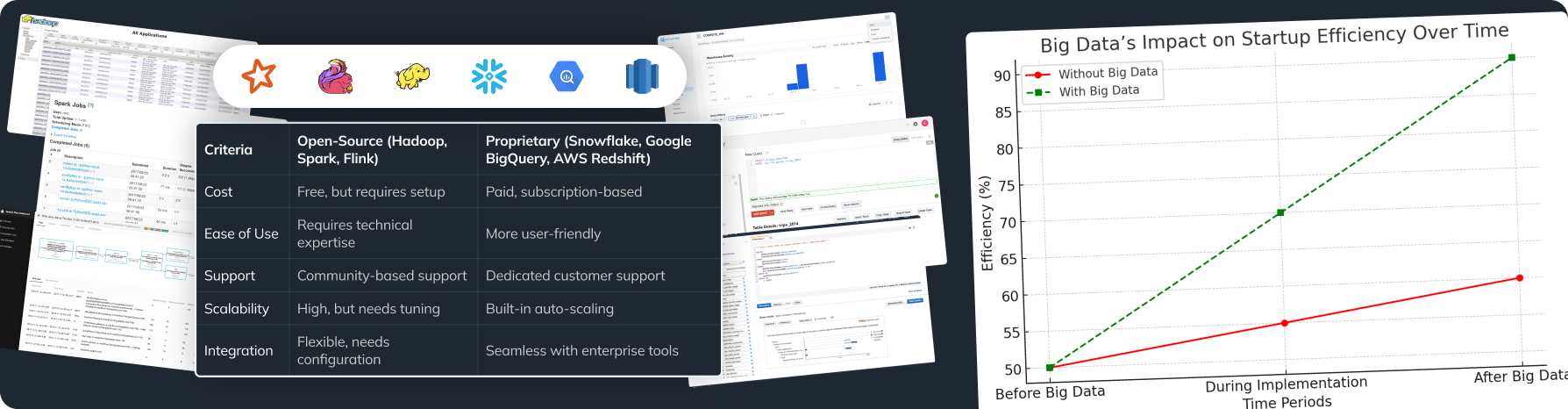
Customer Data Management Tools: Introduction to CDPs
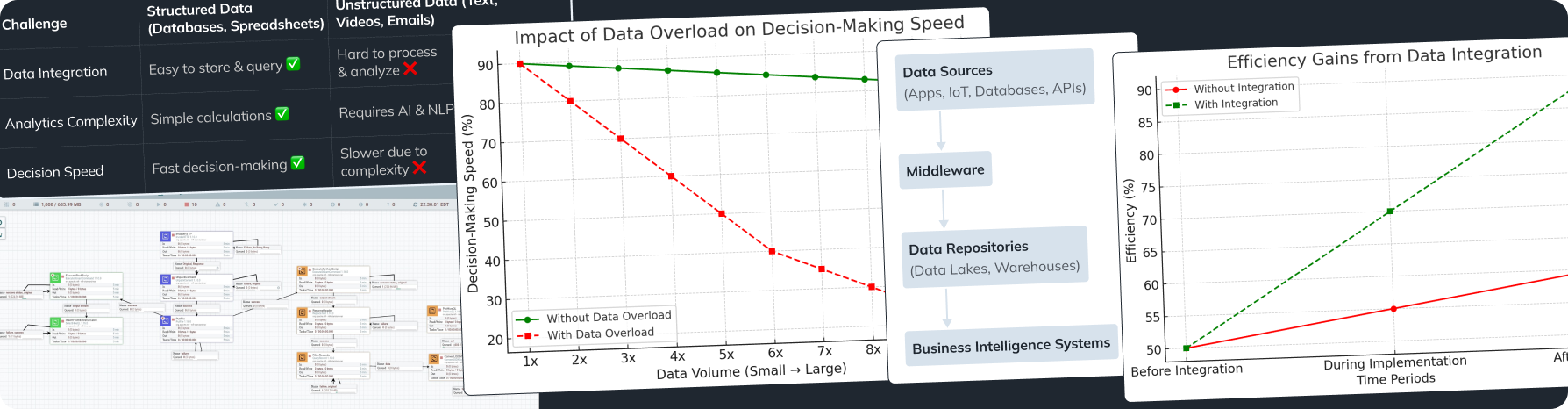
Customer Data Platforms (CDP) are platforms that collect, unify, and analyze customer data from various sources. CDPs allow for creating a single customer profile, significantly simplifying marketing personalization.
Key Functions of CDPs
- Data Collection: CDPs gather customer data from various sources, including CRM, websites, mobile apps, social networks, and more.
- Data Unification: CDPs unify this data into a single customer profile, providing a complete view of their interactions with the brand.
- Data Analysis: CDPs enable data analysis to identify trends, segment customers, and create personalized campaigns.
- Data Activation: CDPs integrate with other marketing tools, allowing the use of data to create personalized messages and offers.
Benefits of Using CDPs
- Unified Data Source: All customer data is stored in one place, simplifying access and analysis.
- Personalization: CDPs enable the creation of personalized marketing campaigns, increasing their effectiveness.
- Improved Customer Experience: A deep understanding of customer needs allows companies to provide better service.
- Increased ROI: Investments in CDPs pay off through increased sales, improved customer loyalty, and optimized marketing spend.
4. Implementation Steps for a First-Party Data Strategy
Setting Up Data Collection Systems
Establishing a data collection system is foundational for successful data use in marketing. A properly configured system allows you to collect high-quality and relevant data necessary for informed decisions.
Steps to Set Up Data Collection
- Define Objectives:
- Clearly articulate what you want to learn from the data. Increase sales? Improve customer engagement? Optimize advertising campaigns?
- Choose key metrics that will indicate goal achievement (conversion rate, average order value, time on site, etc.).
- Select Tools:
- Website Analytics: Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, etc.
- CRM Systems: For storing customer information and interactions.
- Marketing Automation: Automate marketing processes and collect data on campaign interactions.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDP): To unify data from various sources and create a single customer profile.
- Data Collection:
- Website: Install tracking codes for analytics tools, set up events (clicks, page views, cart additions, etc.).
- CRM: Configure automatic data collection on customer interactions (calls, emails, deals).
- Social Media: Use social media analytics tools to collect data on your audience and content interactions.
- Mobile Apps: Use analytics tools for mobile apps to track user behavior.
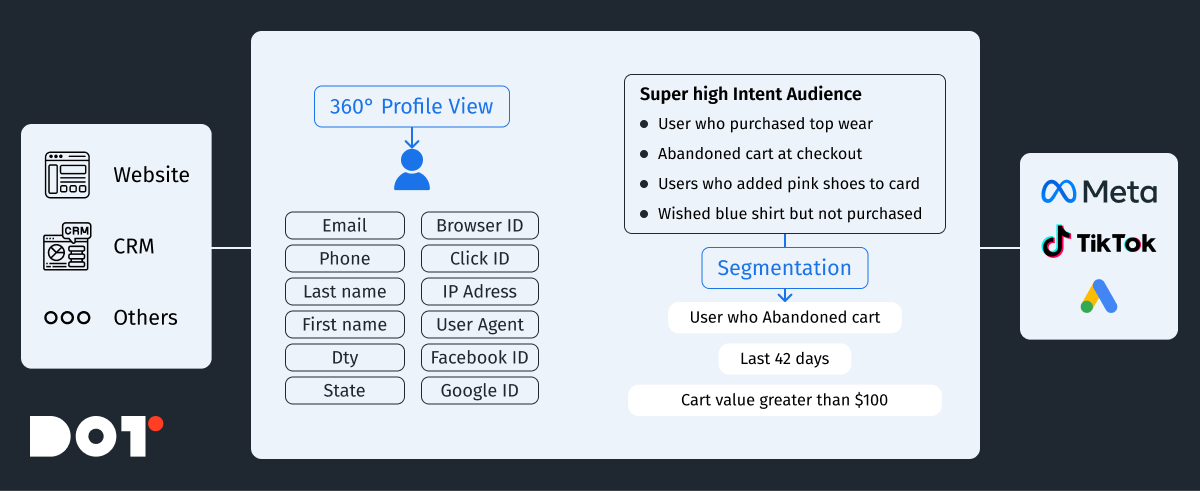
- Data Structure:
- Create a Unified User Identification System: Use unique identifiers to track users across devices and channels.
- Define Key Attributes: Collect data on demographics, behavior, interests, and other important customer attributes.
- Data Standardization: Bring data to a unified format to ensure compatibility and ease of analysis.
- Structure Data: Create a logical data structure that’s convenient for analysis and use.
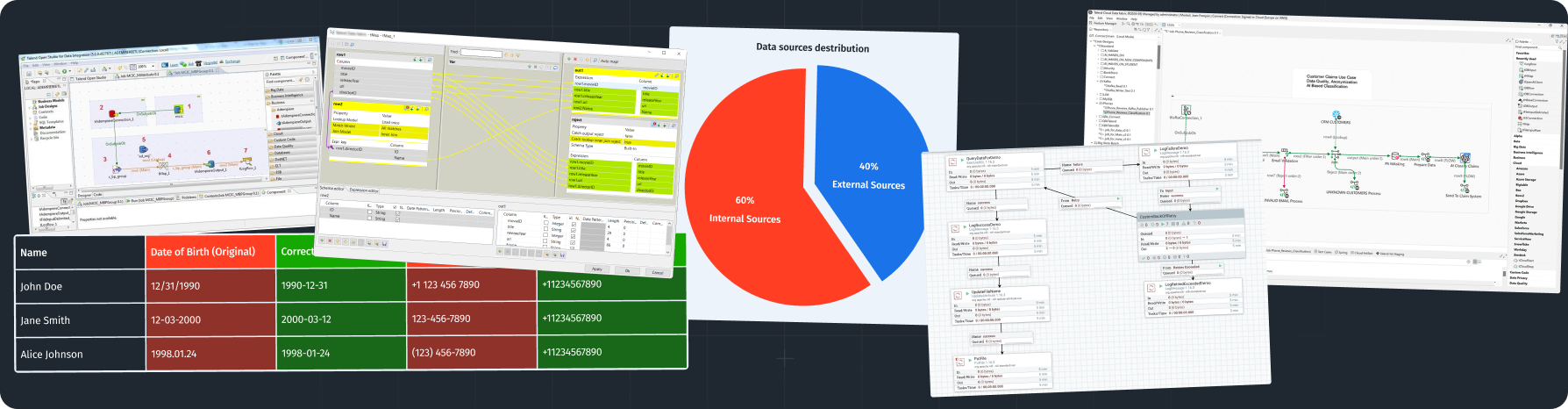
- Data Quality:
- Data Cleaning: Remove duplicates, fill in gaps, correct errors.
- Accuracy Verification: Regularly check data accuracy and adjust as needed.
- Create a Unified Customer Profile: Combine data from various sources into a single customer profile to get a holistic view of their behavior.
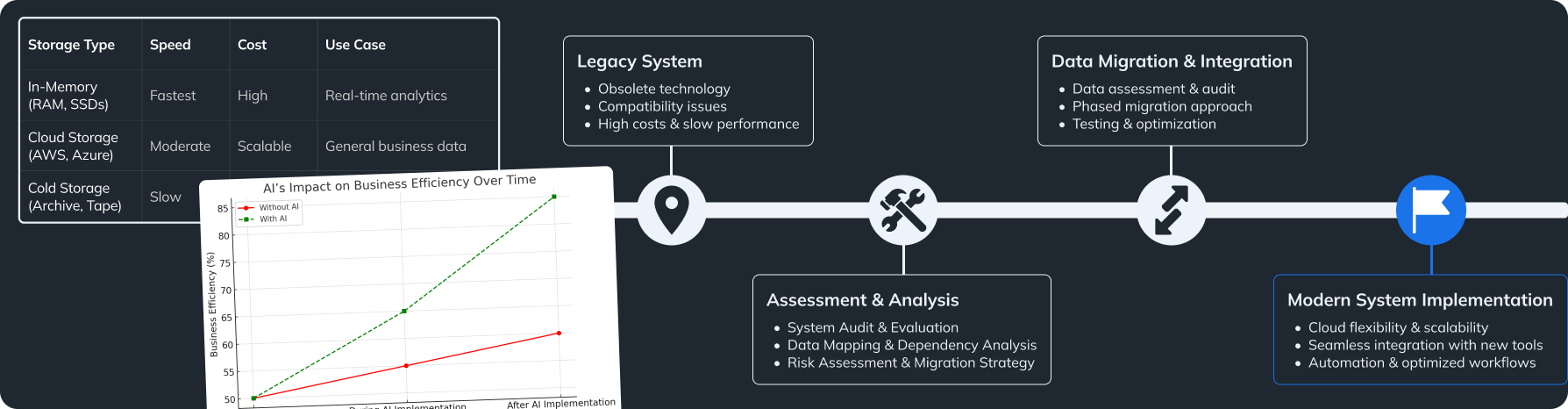
- Data Security:
- Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect against unauthorized access.
- Access Restriction: Provide data access only to authorized users and limit their rights according to the principle of least privilege.
- Legal Compliance: Familiarize yourself with current personal data protection laws (GDPR, CCPA, etc.) and align your processes with requirements.
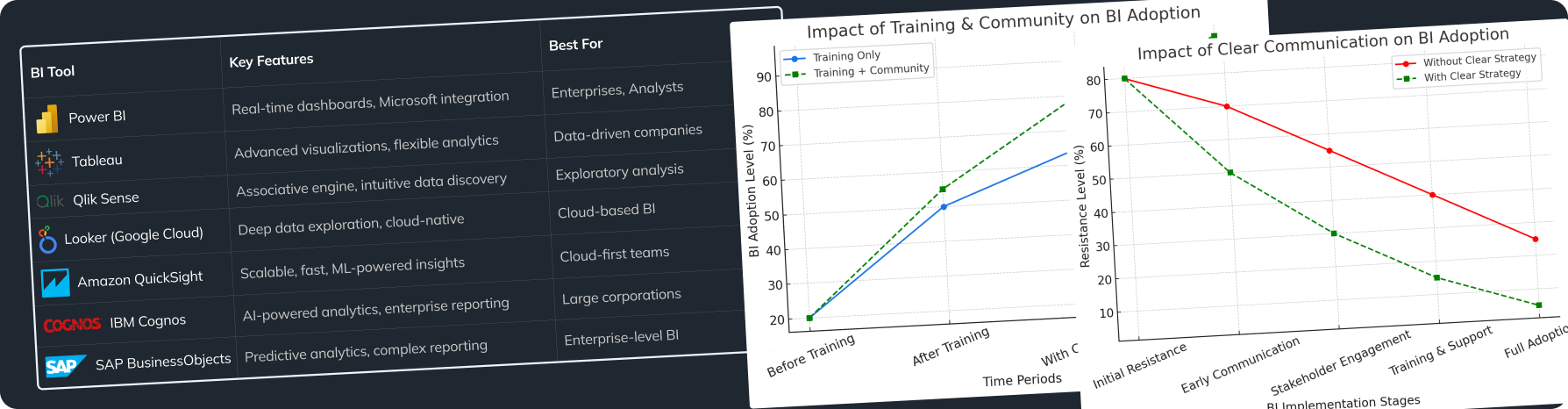
Employee Training
- Develop Individual Training Plans:
- Create personalized training plans for each employee based on their role and existing skills.
- Implement Mentorship:
- Assign mentors to newcomers for support and guidance.
- Build a Data Culture:
- Promote the development of a data culture within the organization where data is considered a valuable asset.
Key Training Areas
- Statistical Data Analysis Methods: Regression analysis, cluster analysis, time series, etc.
- Data Analysis Tools: Excel, Python, R, SQL, specialized data analysis software.
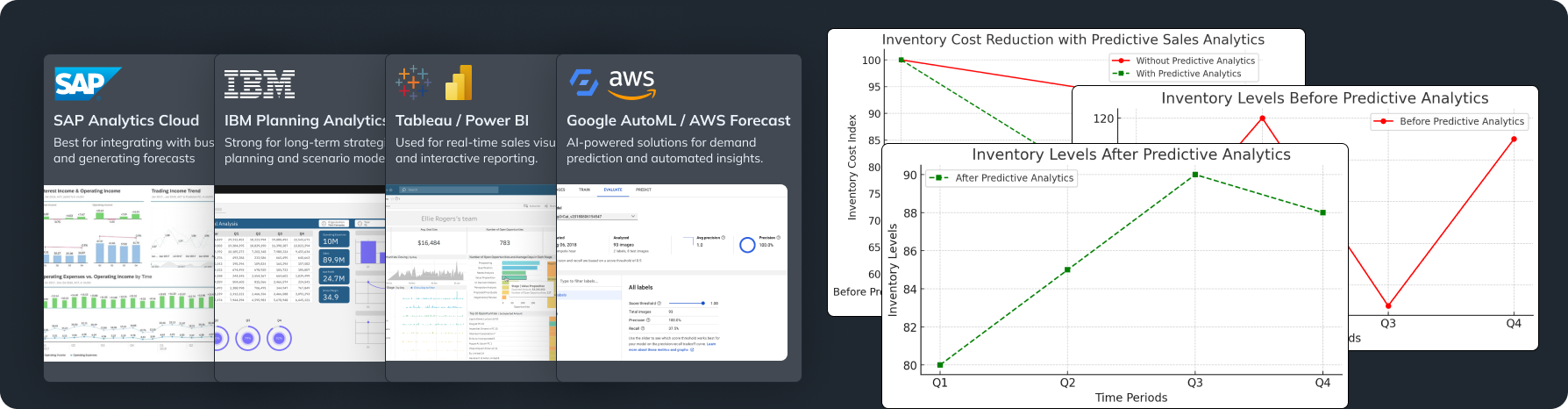
- Data Visualization: Tableau, Power BI, Google Data Studio.
- Machine Learning: Algorithms for prediction and classification.
Recommendations
- Start Small: Don’t try to collect all possible data at once. Begin with key metrics and gradually expand data collection.
- Automation: Automate as many data collection and processing processes as possible.
5. Best Practices and Challenges in First-Party Data Strategy
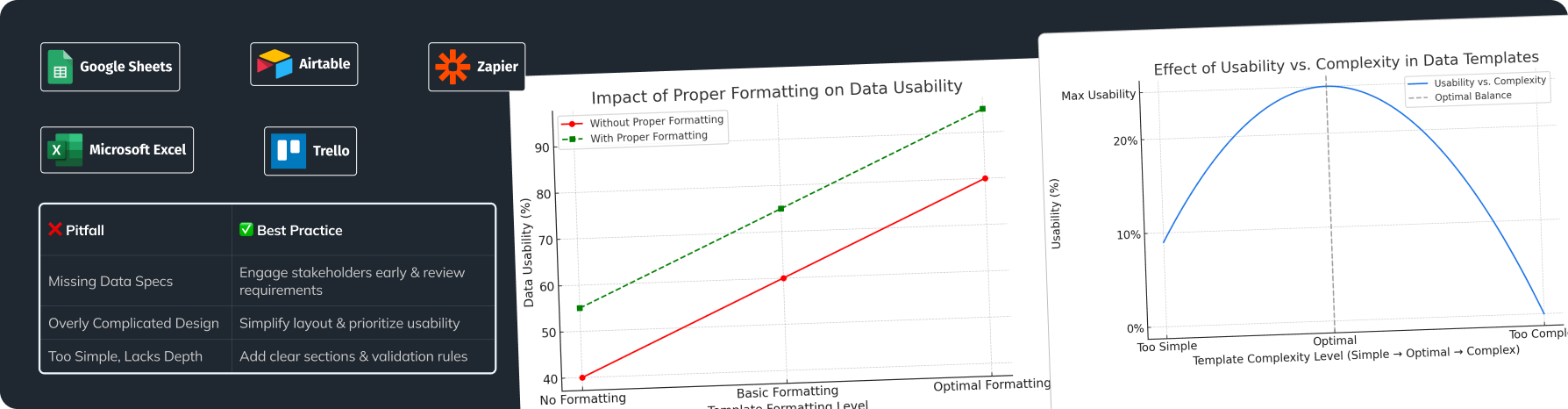
Data Quality and Verification Strategy
Data quality is the foundation for making informed business decisions. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to erroneous conclusions and costly mistakes. Here are key strategies to maintain data accuracy and relevance.
Strategies for Ensuring Data Quality
- Standardization and Unification:
- Unified Glossary: Create a common dictionary of terms and concepts used in the organization.
- Data Format Standardization: Standardize data formats (dates, numbers, currencies).
- Metadata Creation: Describe data structures and content for better understanding.
- Data Verification:
- Validation: Check data for compliance with specific rules and constraints.
- Profiling: Analyze data to identify anomalies and deviations.
- Data Matching: Compare data from different sources to identify inconsistencies.
- Data Cleaning:
- Duplicate Removal: Eliminate duplicate records.
- Gap Filling: Fill in missing data with the most probable values.
- Error Correction: Correct incorrect or incomplete data.
- Data Integration:
- ETL Processes: Extract, transform, and load data from various sources.
- Master Data Management: Create a single source of truth for key entities (customers, products).
- Data Quality Monitoring:
- Key Quality Indicators: Define metrics to assess data quality (completeness, accuracy, relevance).
- Dashboards and Reports: Visualize data to track quality changes.
- Automation: Use tools for automatic detection of data quality issues.
- Metadata Management:
- Data Documentation: Create and update metadata for each dataset.
- Data Catalogs: Organize metadata in a single repository.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Using first-party data is a powerful tool, but challenges are inevitable. Here are the most common ones and ways to overcome them:
- Data Quality Issues:
- Problem: Incomplete, inaccurate, duplicate, or inconsistent data.
- Solution:
- Data Cleaning: Remove duplicates, fill gaps, correct errors.
- Standardization: Bring data to a unified format and structure.
- Validation: Check data for compliance with certain rules.
- Profiling: Analyze data to identify anomalies.
- Lack of a Unified Data System:
- Problem: Data is scattered across different systems and databases.
- Solution:
- Create a Unified Data Repository: Centralize data for easy access and analysis.
- Use ETL Processes: Extract, transform, and load data from various sources.
- Master Data Management: Create a single source of truth for key entities.
- Lack of Employee Skills:
- Problem: Employees lack the necessary knowledge to analyze and use data.
- Solution:
- Training: Conduct workshops and seminars on data handling.
- Mentorship: Assign experienced employees as mentors to newcomers.
- User-Friendly Tools: Choose tools that don’t require deep technical knowledge.
- Absence of a Data Culture:
- Problem: The organization doesn’t understand the importance of data and its role in decision-making.
- Solution:
- Awareness: Hold presentations and workshops on the benefits of using data.
- Leadership Example: Management demonstrates the importance of data through their actions.
- Data Integration in Processes: Use data for everyday decision-making.
- Data Security Risks:
- Problem: Risk of data leaks, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks.
- Solution:
- Encryption: Protect data at rest and in transit.
- Access Control: Limit data access to authorized users only.
- Backups: Regularly create data backups.
- Security Monitoring: Constantly monitor system security.
- Lack of a Data Usage Strategy:
- Problem: No clear plan on how to use data to achieve business goals.
- Solution:
- Define Objectives: Clearly state what business problems can be solved with data.
- Choose Metrics: Determine key performance indicators.
- Develop an Action Plan: Create a step-by-step strategy implementation plan.
- Time and Resource Constraints:
- Problem: Lack of time and resources for data work.
- Solution:
- Automation: Use tools to automate routine tasks.
- External Experts: Hire consultants for complex tasks.
- Prioritization: Focus efforts on the most important projects.
Future-Proofing Data Strategies
To keep your first-party data strategy relevant, it’s necessary to continuously adapt to changes in technology and regulatory environments.
- Monitor New Technologies: Stay updated on new tools and technologies that can improve data processes.
- Adapt to Legal Changes: Keep abreast of the latest changes in data protection legislation and adjust your processes accordingly.
- Flexibility in Planning: Be prepared to adjust your strategy based on changing business goals and customer needs.
- Continuous Learning: Encourage employees to continuously learn and develop their skills.
6. Examples of Successful First-Party Data Strategies
Industry leaders have long realized that first-party data strategy is the golden key to success in modern marketing. Let’s look at some examples of companies that have successfully implemented first-party data strategies and the valuable lessons they’ve learned.
Company Examples
- Netflix:
- Strategy: Analyzes user preferences to create original content and recommend movies and series likely to interest viewers.
- Outcome: Increased user engagement and subscription retention through personalized recommendations.
- Amazon:
- Strategy: Uses purchase data and user behavior to offer personalized recommendations, create targeted advertising campaigns, and optimize logistics chains.
- Outcome: Enhanced customer experience leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.
- Google:
- Strategy: Utilizes search data and other user interactions to improve search results, develop new products, and deliver targeted advertising.
- Outcome: Maintains leadership in search and advertising by providing relevant results and ads.
- Uber:
- Strategy: Uses location data, ride demand, and driver behavior to optimize routes, pricing, and order distribution.
- Outcome: Improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Nike:
- Strategy: Leverages data from fitness trackers to create personalized training programs and motivate customers.
- Outcome: Strengthened brand loyalty and increased product usage.
- Walmart:
- Strategy: Uses sales data to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and improve supply chain planning.
- Outcome: Reduced costs and improved product availability.
Lessons Learned
- Personalization Is Key:
- Deep Customer Understanding: The more you know about your customers, the more personalized offers you can make.
- Content Relevance: Personalized content increases engagement and conversion.
- Improved Customer Experience: Personalization makes brand interaction more enjoyable.
- Data Is an Asset:
- Invest in Infrastructure: Build robust systems for data collection, storage, and analysis.
- Data Security: Prioritize protecting data from leaks and unauthorized access.
- Continuous Updating: Regularly update and enrich data.
- Data Culture:
- Employee Training: All employees should understand the importance of data and know how to use it.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data should form the basis of strategic decisions.
- Experimentation and Iteration: Don’t fear experimenting and constantly improving models based on results.
- Data Integration with Marketing:
- Unified Customer Profile: Combine data from various sources to create a single customer view.
- Marketing Automation: Use automated systems for marketing campaign personalization.
- Marketing Channel Attribution: Evaluate the effectiveness of different marketing channels based on data.
Key Takeaways for Marketers
- Data Is the New Oil: Companies that effectively use their data gain a significant competitive advantage.
- Personalization Drives Success: Understanding individual customer needs allows for creating more valuable offers.
- Continuous Improvement: Data analysis is an ongoing process requiring constant development and adaptation.
7. Conclusion and Next Steps
Implementing a robust first-party data strategy is essential in today’s market:
- Better Decision-Making: Reliable data leads to effective strategies.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalization improves satisfaction.
- Increased Marketing Efficiency: Optimizes spend and improves ROI.
Key Elements of a Successful Data Strategy
- Data Collection and Storage: Systematic collection from various sources and creating a unified repository.
- Data Cleaning and Preparation: Removing duplicates, filling gaps, standardizing formats.
- Data Analysis: Using statistical methods to identify patterns and make forecasts.
- Data Visualization: Converting complex data into understandable visuals.
- Personalization: Creating individualized offers based on customer behavior.
- Experimentation and Optimization: Continuously testing and improving campaigns.
- Data Culture: Fostering a culture where data is a valuable asset used in decision-making.
- Data Security: Ensuring protection from unauthorized access and breaches.
Reflect on Your Approach
- How do you collect and store customer data?
- How often do you analyze this data, and what conclusions do you draw?
- How personalized are your marketing campaigns?
- Do you use data to optimize business processes?
If you’re unsure about your answers, it’s a great signal to start taking action!
At Dot Analytics, we specialize in helping businesses develop and implement effective first-party data strategies. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in unlocking the full potential of your data.
Do you fully understand the topic? If not, you can book a free 15-minute consultation with CEO of Dot Analytics.



















Leave a Reply